Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition requiring immediate attention where the embryo implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube. This article presents the 5 common signs of an ectopic pregnancy, offering evidence-based information and expert insights.
By identifying these symptoms—ranging from abnormal vaginal bleeding to sharp abdominal pain—we provide a vital solution for women to recognize this condition promptly. The information is drawn from medical research and clinical experiences, serving as reliable proof and guidance to address this critical health issue effectively.
1. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding

One of the earliest signs of an ectopic pregnancy is abnormal vaginal bleeding. This is not your typical menstrual period. It’s usually lighter, darker, or more watery. This type of bleeding often confuses women, as it can be mistaken for a light period.
However, it’s essential to pay attention to any deviation from your normal menstrual pattern. This bleeding may be intermittent or continuous and is sometimes accompanied by pelvic discomfort. Unlike normal menstrual blood, this bleeding might contain clots or tissues.
If you notice such changes, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for an evaluation.
2. Pelvic or Abdominal Pain
Pain is a red flag in any pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, the pain is usually sharp and stabbing. It might be felt on one side of the body, corresponding to the affected fallopian tube. This pain can become more severe with movement or straining and should not be ignored.
It often worsens over time and may vary in intensity. Sometimes, this pain might be misinterpreted as a normal part of early pregnancy, but its unilateral nature and sharp quality are key differentiators. If such pain persists or escalates, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial to rule out this condition.
3. Shoulder Tip Pain

An unusual but significant symptom of ectopic pregnancy is shoulder tip pain. This pain occurs where your shoulder ends and your arm begins. It’s a result of bleeding in the abdomen, which irritates the diaphragm, and is a warning sign of internal bleeding.
This symptom requires immediate medical attention. The pain may be more noticeable when lying down or taking deep breaths. It’s different from typical muscle pain and can be quite distressing. It’s a direct indication of bleeding into the abdominal cavity, which can rapidly become a life-threatening situation.
4. Gastrointestinal Symptoms

Women with an ectopic pregnancy may experience gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms can mimic those of a normal early pregnancy, but when coupled with other signs, they can point toward this condition.
These symptoms are often mistaken for common stomach ailments or food-related issues. However, if they occur alongside other signs like abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain, they should be taken seriously.
It’s crucial to understand that gastrointestinal symptoms in the context of a possible pregnancy should always warrant a medical evaluation, especially if they deviate from typical pregnancy-induced discomforts.
5. Fainting or Dizziness

As the ectopic pregnancy progresses, the risk of a ruptured fallopian tube increases. This can lead to significant internal bleeding, causing fainting, dizziness, or even shock. These are severe symptoms indicating an emergency situation.
Fainting episodes may be brief, but they are a sign that the body is under significant stress. Dizziness and lightheadedness, especially when standing up, can be early signs of internal bleeding. In such scenarios, immediate medical intervention is essential as these symptoms indicate a critical and potentially life-threatening condition.
How Is It Treated?
Treating an ectopic pregnancy is crucial because it cannot proceed normally and poses significant health risks. The treatment approach depends on several factors, including the stage of the pregnancy, the patient’s symptoms and overall health, and whether there’s been a rupture. Here are the primary treatment methods:
Medication
If the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and there’s no immediate risk of rupture, a drug called methotrexate may be used. Methotrexate inhibits the growth of rapidly dividing cells, like those in the developing embryo.
This treatment allows the body to absorb the pregnancy tissue and can prevent the need for surgery. It’s important to monitor hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) levels after treatment to ensure the pregnancy has been fully resolved.
Surgery
In cases where there’s a risk of rupture or if the ectopic pregnancy has already caused a rupture, surgery is necessary. The most common surgical procedure is laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgery where small incisions are made in the abdomen to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
In more severe cases, or if there’s significant bleeding, a more extensive surgical procedure called a laparotomy may be required.
Monitoring and Follow-up
After the treatment, close monitoring is essential. This usually involves blood tests to measure hCG levels, ensuring they return to pre-pregnancy levels, indicating that the ectopic tissue has been fully absorbed or removed.
Future Fertility Considerations

One of the concerns after an ectopic pregnancy is the impact on future fertility. This depends on the extent of the damage to the fallopian tubes and the type of treatment received. In many cases, successful pregnancies are possible, but the risk of another ectopic pregnancy is higher.
Emotional Support and Counseling
Experiencing an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally traumatic. Counseling and support from healthcare providers, mental health professionals, and support groups can be beneficial for recovery.
What can cause an ectopic pregnancy?
1. Fallopian Tube Damage
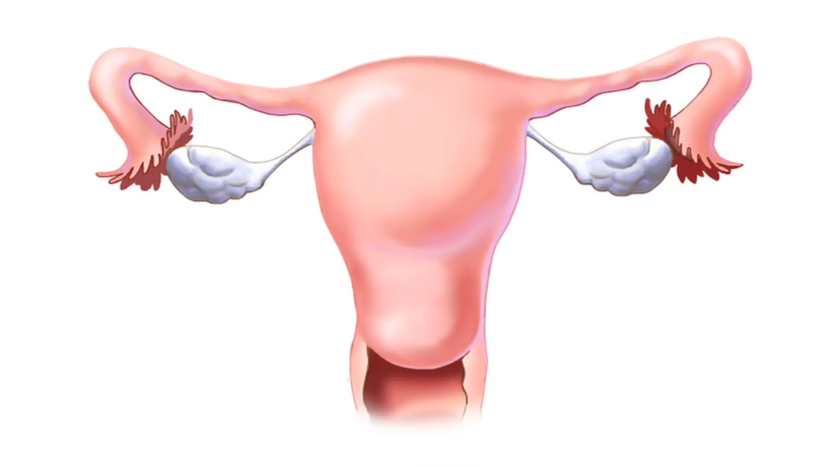
The most common cause of an ectopic pregnancy is damage to the fallopian tubes. Damaged or scarred fallopian tubes can hinder the movement of a fertilized egg to the uterus, leading to implantation in the tube.
This damage can result from a variety of factors, such as a previous ectopic pregnancy, surgery in the pelvic area, or infections like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), often caused by sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
2. Hormonal Factors
Hormonal imbalances or abnormal development of the fertilized egg can lead to ectopic pregnancies. Women undergoing fertility treatments or using fertility medications that stimulate ovulation may also have an increased risk.
3. Intrauterine Device (IUD)
While IUDs are highly effective at preventing intrauterine pregnancies, if a pregnancy does occur with an IUD in place, there’s a higher chance of it being ectopic. However, the overall risk of an ectopic pregnancy is lower in IUD users compared to those not using any contraception.
4. Smoking

Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. The substances in cigarettes can affect the functioning of the fallopian tubes, interfering with the transport of the egg.
5. Previous Surgery
Surgeries in the pelvic area, including tubal surgery or a previous ectopic pregnancy surgery, can increase the risk due to potential damage or scarring of the fallopian tubes.
6. Age
Women over the age of 35 have a higher risk of ectopic pregnancies. The risk increases with age, likely due to factors like decreased egg quality and changes in the reproductive system.
7. Endometriosis
This condition involves the growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus and can lead to blockages or damage in the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
Being Pregnant Again
Trying for another baby after an ectopic pregnancy is a significant decision that involves both physical and emotional considerations. Doctors often recommend waiting a certain period before trying to conceive again. This period can vary depending on the treatment you received.
For instance, after treatment with methotrexate, it’s typically advised to wait at least three months due to the drug’s effect on folate levels, which are crucial for a healthy pregnancy. If you had a fallopian tube removed or if there was significant damage, a fertility evaluation might be suggested.
This can include tests to assess the health of your remaining fallopian tube and overall fertility status. Adopt a healthy lifestyle to enhance fertility and prepare your body for a future pregnancy. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol and caffeine intake, and taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid.
FAQs
Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of an ectopic pregnancy?
While some risk factors like previous medical conditions, cannot be altered, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce risk. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective changes, as smoking is a known risk factor.
Maintaining a healthy weight and managing chronic conditions, like diabetes, can also contribute to overall reproductive health.
Are there any specific symptoms that differentiate an ectopic pregnancy from a miscarriage in the early stages?
Ectopic pregnancies and miscarriages can have overlapping symptoms, such as vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. However, the specific sharp, stabbing pain on one side of the abdomen, and shoulder tip pain are more indicative of an ectopic pregnancy.
Miscarriages typically involve cramping and bleeding that resembles a heavy menstrual period.
Is it possible to have an ectopic pregnancy with a normal intrauterine pregnancy at the same time?
Yes, though rare, it’s possible to have a heterotopic pregnancy, where one embryo implants in the uterus and another implant ectopically, usually in a fallopian tube. This is more common in pregnancies achieved through assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
How does an ectopic pregnancy impact future fertility?
The impact on fertility depends on the treatment received and the extent of damage to the reproductive organs. If one fallopian tube is removed, the other tube can still function. However, if both tubes are damaged or removed, natural conception becomes difficult and assisted reproductive techniques like IVF may be needed.
Can ectopic pregnancies be prevented?
While it’s not possible to prevent an ectopic pregnancy entirely, reducing risk factors can help. This includes regular sexual health check-ups to prevent and treat sexually transmitted infections, avoiding smoking, and ensuring any existing health conditions are well-managed.
Are there any long-term health implications after an ectopic pregnancy?
Apart from potential impacts on fertility, most women do not experience long-term health issues after this condition. However, it’s important to monitor for and address any emotional or psychological effects, as the experience can be traumatic. Regular follow-ups and a supportive environment are beneficial for overall well-being.
Summary
In conclusion, ectopic pregnancies, while rare, are serious conditions that require immediate medical attention. Key signs include abnormal vaginal bleeding, sharp pelvic or abdominal pain, shoulder tip pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and fainting or dizziness.
Treatment options vary based on the pregnancy stage and include medication, surgery, or a combination. After an ectopic pregnancy, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals about the right time to try for another baby and understand the associated risks.
Lifestyle changes and early monitoring in subsequent pregnancies can help manage these risks.